Lyme Disease And Oral Health
Did you know that the health of your mouth is directly linked to your overall health? It’s not just about having bright teeth and fresh breath, but also about preventing and detecting diseases that can manifest in your oral cavity. This is especially true for patients with Lyme disease, a bacterial infection commonly transmitted through tick bites. In this article, we’ll explore the various ways in which Lyme disease can affect our oral health, from inflammation to dental issues and beyond. By understanding the connection between Lyme disease and oral health, patients can prioritize early detection and treatment to effectively manage their symptoms.
Lyme disease is a multisystem disorder that can cause a wide range of symptoms, including fever, fatigue, joint pain, and headache. While these symptoms often receive the most attention, there are also numerous oral symptoms that can indicate Lyme disease. One of the most common symptoms is dry mouth, which can occur when the salivary gland becomes inflamed. Other symptoms, such as pulp inflammation and burning mouth syndrome, may also be related to Lyme disease. By recognizing and addressing these oral symptoms early on, patients can receive appropriate treatment and improve their overall health outcomes.
In addition to oral symptoms, Lyme disease can also lead to temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction. TMJ is a condition that affects the hinge connecting the jaw to the skull, potentially causing discomfort and difficulty with opening or closing the mouth. Interestingly, there is a link between TMJ dysfunction and Lyme disease, although the exact mechanisms of this relationship are not yet fully known. Regardless, it is crucial for patients with Lyme disease to seek proper diagnosis and treatment to manage their TMJ symptoms effectively.
Lyme disease can also increase the risk of dental health issues, such as periodontal disease. This may be due to bacteria from the original bite site entering the mouth and causing inflammation. Patients with Lyme disease may also be more susceptible to gingivitis, a common form of periodontal disease that can lead to bleeding and swelling of the gums. Furthermore, patients with post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTLDS) may experience worsened symptoms after tooth extractions, underscoring the importance of careful monitoring and management by both dental and medical professionals.
Collaboration between medical and dental professionals is crucial for patients with Lyme disease and their overall health outcomes. Dental professionals can screen for early detection of oral symptoms and provide preventative care to minimize the risk of dental issues. Medical professionals can diagnose and treat Lyme disease and its various symptoms, ensuring optimal symptom management and improving overall quality of life. Patients can also play an active role in their own healthcare by recognizing the symptoms of Lyme disease and seeking early intervention to maximize treatment effectiveness.
Conclusion
Overall, it is clear that Lyme disease can have significant impacts on our oral health. From initial symptoms like dry mouth and inflammation to dental issues like gingivitis and PTLDS, the connection between Lyme disease and oral health cannot be ignored. By recognizing and addressing these symptoms early on and working collaboratively with healthcare providers, patients with Lyme disease can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Trending News
-
Non Toxic Dental Fillings : BPA, BHT, HMBP, DPCL, TPSb, HEMA, TEGDMA Free Admin
-
Essential Questions for Your Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon Admin
-
Regenerative Endodontics Admin
-
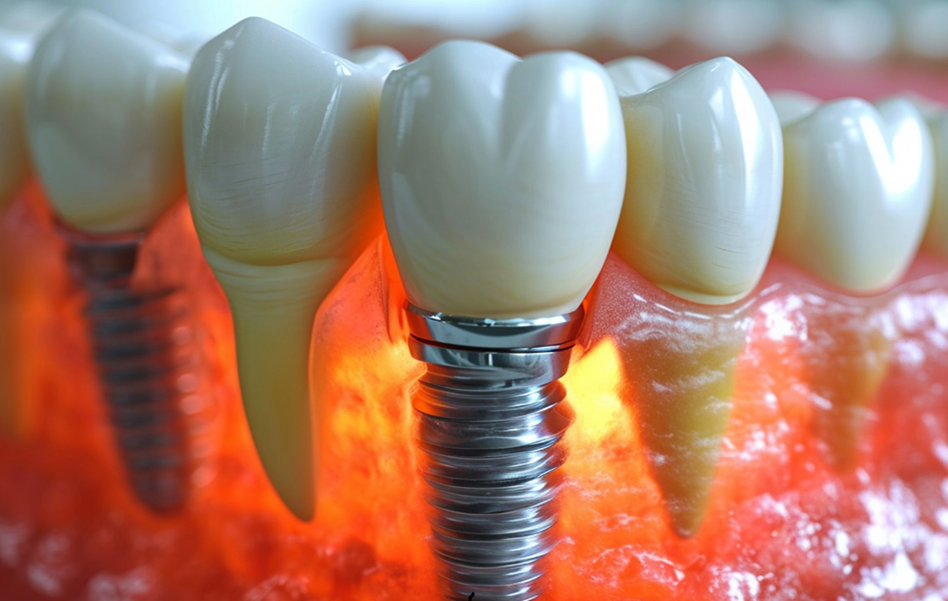
Understanding the Risks and Causes of Dental Implant Failures Admin
-

Why Root Canals Fail? | The Usual Suspects Meredith Y. Newman Endodontist Fresno
